In 2026, a dealership’s operating margin depends on how quickly leadership can turn reliable information into decisions. For CEOs, the challenge isn’t just performance—it’s ensuring the organization runs on consistent data ...
Explore In-Depth CEO Insights and Articles
Explore our extensive collection of articles featuring the latest insights, trends, and success stories from top business leaders. Stay informed with expert analysis and in-depth content that covers a wide range of topics in leadership and innovation. Browse now to stay ahead in the business world.

Browse Our Latest Articles
Explore the latest articles, featuring expert insights, groundbreaking innovations, and success stories from visionary business leaders. From leadership strategies to industry trends, our articles deliver the knowledge you need to stay informed and inspired. Dive in and stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of business leadership.
Shipping protection is an important issue to the companies which offer physical products online or offline via distributors. A packaging method that involves placing a product in a smaller box, and enwrapping it inside a bigger outer box with cush...
Expanding into Canada offers businesses access to a skilled workforce, a stable economy, and a favourable regulatory environment. However, hiring employees without a local entity can be complex. Canada’s employment landscape varies by province, re...
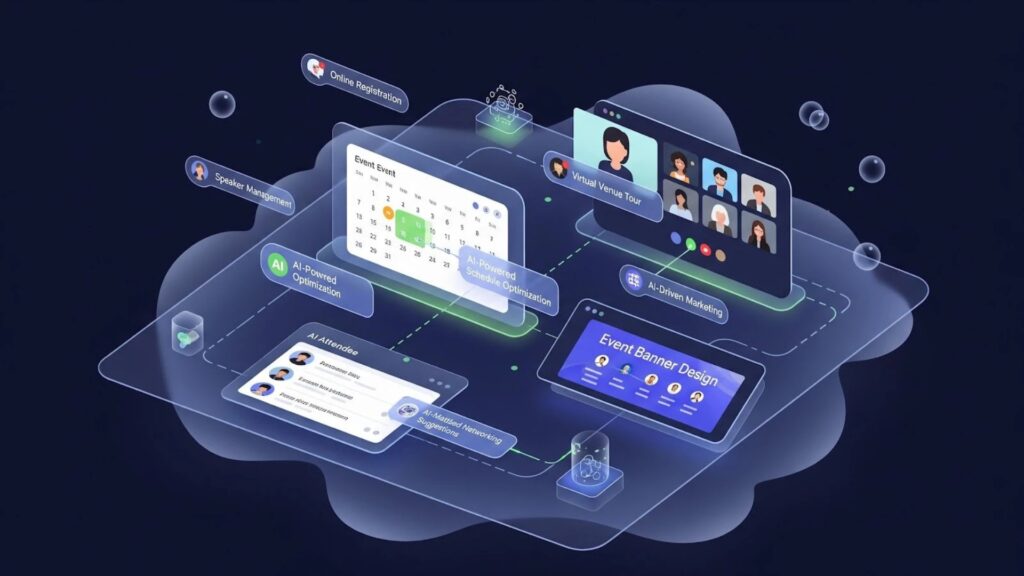
Planning a business event used to feel like juggling all at once. You had spreadsheets for your guest list, a dozen email threads with vendors, and a constant fear that you forgot something crucial. But things have changed. We aren't just wor...
Procurement in today's hectic business world encompasses more than just purchasing goods and services. Organisations can maximise spending, uphold compliance and facilitate rapid business unit operations by implementing effective procurement ...
Sam Seigler shares why resilient, adaptable leadership is now central to business continuity and what organisations should be looking for when appointing senior executives in turbulent times.
Inclusive hiring practices fill business needs, rather than being a business social responsibility initiative. They are about seeking access and talent that many firms are passing over, building stronger teams, and reflecting the diversity of cust...
Vehicle finance might have once been a fairly routine operational decision. However, in recent times, it has become a strategic lever that intersects with everything from capital allocation and risk governance to ESG commitments and balance sheet ...
Planning a team-building event sounds simple — that is, until you are the one responsible for making it memorable. Too often, these gatherings feel forced or predictable, which makes employees check out before they even arrive. When done rig...
Plans often fail because teams do not feel involved. Tools for collaboration in strategic planning are essential from the start, especially when leadership designs a strategy without shared context. When employees lack visibility into goals and de...
Clear communication drives revenue, trust and long-term growth. When customers, partners or employees struggle to communicate in a shared language, businesses face delays, misunderstandings and missed opportunities. These aren't minor inconve...
Hiring a Supply Chain Manager for an online retail business isn’t just an operations decision, it’s also a revenue and customer experience decision. If a product is out of stock, customers don’t wait: 69% will buy from a competitor, and 43% will s...